What are AI Agents? The Next Evolution in Nutrition?
AI agents are set to transform the field of personalised nutrition, shifting from static advice to dynamic and interactive coaching.
By Stephanie Tucker MSc ANutr
What is an AI Agent?
AI agents are software entities that perceive their environment through data, analyzes the information and then acts to achieve specific goals [1]. In health, AI agents use machine learning and natural language processing with predictive analytics to interpret health information. AI agents are also known as Agentic AI.
How are AI agents different from AI chatbots?
AI chatbots typically are rule-based tools designed to handle simple conversations and respond to fairly straightforward requests, whereas AI agents are dynamic and autonomous systems capable of reasoning, learning and making complex decisions. A good way to think about it is that AI agents have an almost circular learning pattern - they are able to review and criticise their own work and make improvements.
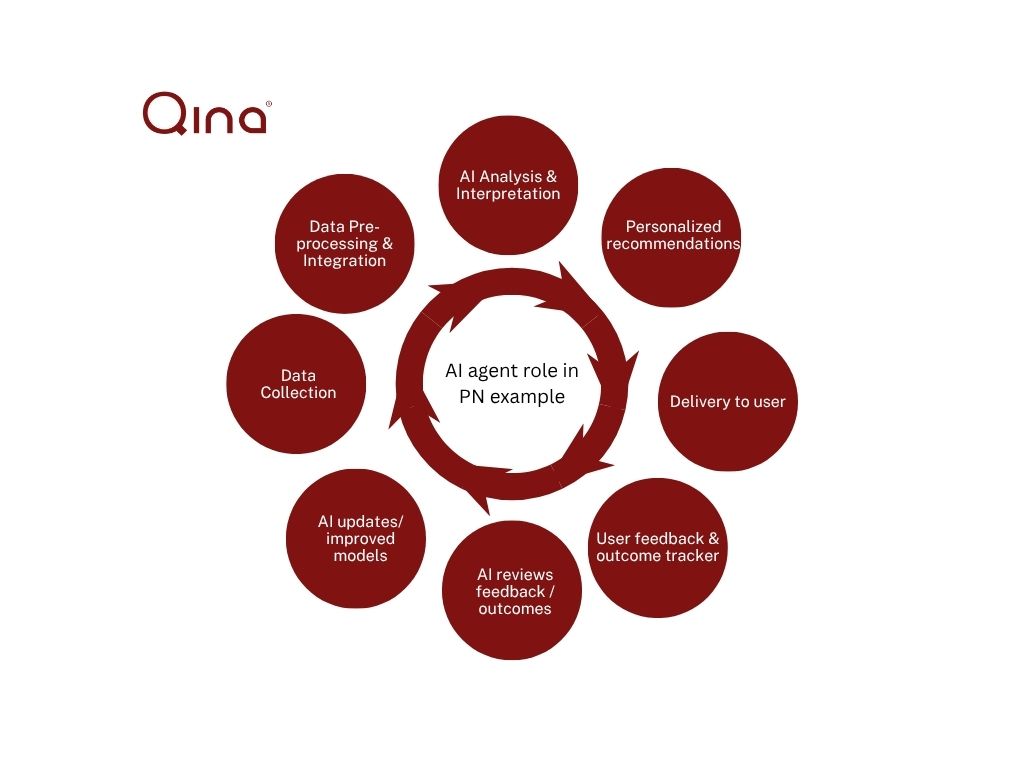
Figure 1. Shows an example of how AI agents may be used to provide personalized health recommendations and how AI agents can evaluate and improve their recommendations based on data analysis and feedback.
Key Differences between AI agents and AI chatbots:
- Task Complexity: AI agents can tackle complex tasks and adapt as situations change, while chatbots are limited to guiding users through predefined flows or answering limited sets of questions.
- Learning and Adaptability: AI agents continuously learn from user interactions and real-world feedback, expanding their capabilities over time; chatbots have limited or no ability to learn unless reprogrammed by developers.
- Autonomy: Agents can proactively initiate actions and make independent decisions, whereas chatbots react only when prompted by user input and follow static scripts.
- Personalization and Context: AI agents leverage user data and context to provide deeply personalized responses and services, while chatbots typically deliver basic personalization (e.g., using a first name) and operate within narrow domains.
- Integration Scope: AI agents often work across multiple platforms, pulling data from various sources to inform decisions, while chatbots usually interact with a single system or database.
- Natural Language Understanding: AI agents use advanced language models to comprehend intent and meaning, supporting more human, flexible conversations, whereas chatbots often get stuck or respond with irrelevant answers if outside their script.
Imagine an AI that watches your habits, learns your goals, and offers you specific tips - before you even ask.
What powers an AI agent?
The enabling tech behind AI agents brings together 4 core pillars:
-
Perception: Integration of data (wearables, food logs, biosensors)
-
Reasoning & Planning: Predicting outcomes and selecting tailored actions
-
Continuous Learning: Gets smarter with every interaction
-
Autonomous Action: Make decisions and follow through
AI Agent in Personalized Nutrition
AI agents can have a range of uses in health and nutrition:
- Provide real-time dietary feedback and recommendations based on continuous data streams.
- Adapt plans as users’ goals, health status, or preferences change over time.
- Improve accuracy and efficacy by integrating genetic, biological, and behavioral data.
AI Agent potential to drive research
AI agents and advancements in data learning allow for enhanced efficiency and accuracy of dietary assessment tools, such as food image classification, estimating portion size and nutrient prediction, which can be used to increase the accuracy of dietary assessment and recommendations. With the ability to analyse large data sets it gives researchers the opportunity to conduct large scale experiments, especially those that look at the effect of personalized recommendations and standardised coaching, with reduced time demands [3].
Researchers can now test new diet recommendations on thousands, not just dozens, of participants - with instant feedback.
In multidisciplinary teams, where dietitians and nutritionists ensure scientific accuracy and data scientists provide sophisticated analytical tools, there is great potential for the role of AI advancing precision nutrition that reflect the variability and diversity of real life [4].
Innovators in leveraging AI Agents for personalised nutrition
There are many companies starting to utilise AI agents, many for interactive coaching but also others for data analysis and adaptive recommendations based on continuous health data from wearables.
Passio.ai - Passio Nutrition software-AI allows the scanning of food items via cameras and provides identification of the item to import the nutritional information into food and lifestyle trackers. The app also carries out volume estimation, and multi-food detection, and provides an AI nutritionist chatbot, barcode scanner, meal plans, recipes, tracking of meals, and other features. Passio AI partners with various service providers to enhance its integration into health and fitness platforms.
Spoon Guru - Spoon Guru’s AI uses behavioral and product data to deliver insightful, satisfying shopping experiences. They have many packages available including Health+ which empowers businesses to partner with their customers in meeting their health goals.
January AI - January AI’s technology uses artificial intelligence to analyze the data collected and provide personalized insights and recommendations. Users can track their blood sugar levels, dietary intake, physical activity, and sleep patterns to better understand their metabolic health.
Inside Tracker - In 2025, InsideTracker launched Terra, a groundbreaking virtual health coach that offers personalized, data-driven wellness guidance based on users' individual health profiles. Building on the success of its previous AI tool, Ask InsideTracker, Terra uses GPT-4 and integrates blood biomarkers, lifestyle data, and genetic insights to deliver tailored recommendations once exclusive to concierge medicine. Users can ask specific health questions, such as how to improve sleep or reduce fatigue, and receive science-backed, individualized advice.
Market Trends
Growth
Major investments are flowing into AI agent startups, and the number of companies leveraging AI in food, health, and nutrition increased by 35% from July 2023 to December 2024 (Qina platform data).
Experimentation
Companies are piloting AI agents for: personalized meal planning (e.g Spoonguru for GLP-1 users), nutrition tracking and recommendations (e.g MyFitnessPal), customer engagement and support (e.g chatbots, WhatsApp agents) and automation of repetitive tasks (e.g telemedicine note-taking for dietitians).
Integration
Next-gen AI agents are becoming multimodal, able to process text, voice, images, and video, and compatible across platforms.
The AI in personalized nutrition sector is forecasted to reach $21.5B by 2034 according to Towards FnB (2025).
Current challenges in using AI Agents in health
AI agents in health hold great promise, but their adoption is hampered by challenges around accuracy, bias, privacy, equity, integration, regulation, and trust. Addressing these issues requires:
- Diverse, high-quality data
- Transparent and explainable algorithms
- Strong privacy and security measures
- Inclusive design and equitable access
- Ongoing human oversight and multidisciplinary collaboration
- Clear regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines
Opportunities for companies and brands
AI agents give companies a lot of opportunity for growth, a major factor is hyper-personalization at scale. The ability to give highly personalized experiences and services to consumers allows companies to expand and provide a service to an increased number of customers without pressure on existing staff. AI agents also facilitate a shift from “direct-to-consumer” to “direct-to-me” models, where consumers control their data and receive tailored value in exchange. It also allows for increased analysis of vast datasets, facilitating accelerated research and development. If companies use AI agents ethically and transparently there is opportunity to increase consumer trust, however there is also risk if there is not clear labelling of their use. Companies and brands that leverage these opportunities, while addressing privacy, ethics, and regulatory requirements, will be best positioned to lead in the next era of consumer engagement and health.
The Qina Take
Today’s AI agents are set to transform the field of personalized nutrition, shifting it from static advice to dynamic, interactive coaching. The combination of advanced algorithms and improved ethical standards means everyone could soon have a data smart, responsive health partner right in their pocket.
References
- IBM The 2025 Guide to AI Agents | IBM
- Towards FnB (2025). AI in Personalized Nutrition Market to Reach USD 21.54
- Agrawal et al, 2025. Artificial intelligence in personalized nutrition and food manufacturing: a comprehensive review of methods, applications, and future directions - PMC
- Bhattamisra et al, 2023. Artificial Intelligence in Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Research
- Passio.ai. Nutrition-AI Hub | Food Logging SDK + REST API + Largest Nutrition Database
- Spoon Guru Home - Spoon Guru
- January AI January AI | Where AI Meets Precision Health
- Inside Tracker Optimize wellness and performance through blood tests, nutrition and science.
